Map Of Venezuela - Major Cities, Regions And Natural Wonders
Understanding the map of Venezuela gives you a deeper appreciation for the country's stunning landscapes and history. From its jungles to its beaches, this map reveals it all.
Author:Finn WildeReviewer:Michael RachalDec 13, 202416.3K Shares388.8K Views
Venezuela, renowned for its stunning landscapes and vibrant culture, has a rich history that reflects its diverse geography. Initially inhabited by indigenous tribes, the region saw European contact beginning with Christopher Columbus in 1498, which led to Spanish colonization. Over the years, Venezuela evolved from a Spanish colony into a republic, marked by struggles for independence and political upheaval.
Today, the country's unique identity is expressed through its music, cuisine, and festivals, shaped by centuries of history. Understanding Venezuela’s cities, regions, and natural wonders reveals invaluable insights into this captivating nation, appealing to travelers and those eager to learn more about this extraordinary part of the world.
Geographical Overview Of Venezuela
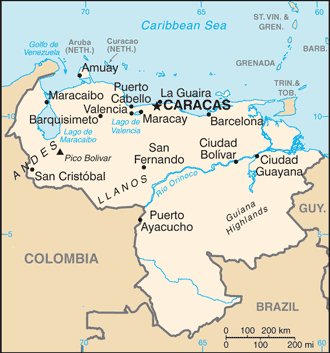
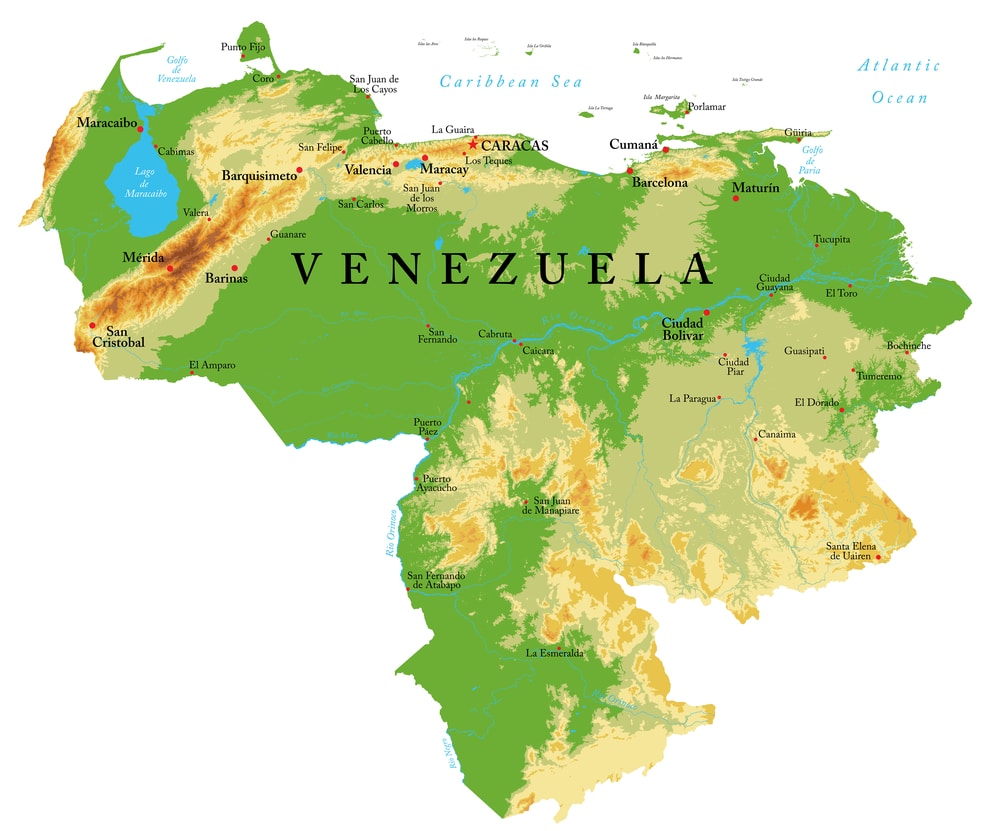
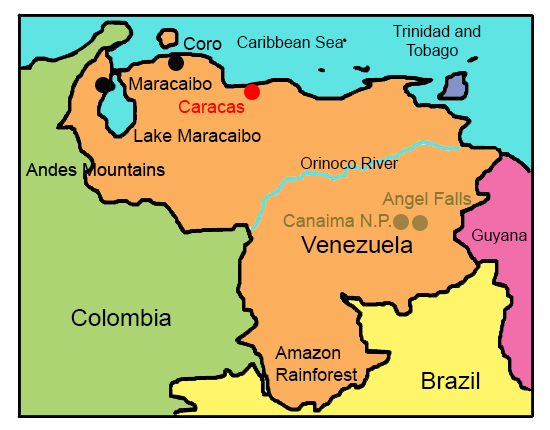
Venezuela is located on the northern coast of South America, bordered by the Caribbean Seato the north, Colombia to the west, Brazil to the south, and Guyana to the east. The country boasts a diverse topography that includes coastal plains, the Andes mountains, extensive lowland regions, and the Amazon rainforest. This geographic diversity not only shapes the climate and ecosystems within the country but also influences the cultural practices of its inhabitants.
The country's most notable geographical feature is the Andes mountain range, which runs along its western border. Venezuela's varied landscapes support a wide range of ecosystems, making it one of the most biodiverse countries in the world. This unique geography plays a significant role in shaping both the environment and the lives of those who call Venezuela home.
Capital Of Venezuela
The capital of Venezuela is Caracas, a bustling metropolis nestled in the Valley of Caracas in the northern part of the country. It is the largest city in Venezuela and serves as the political, economic, and cultural center.
Map Of Venezuela Cities
1. Caracas
Caracas, the capital city of Venezuela, is a vibrant metropolis located in a mountainous valley. Known for its cultural landmarks such as the Teresa Carreño Cultural Complex and the National Pantheon, Caracas is the political and economic center of the country. Its mix of modern skyscrapers and historical architecture offers a unique urban landscape, while its rich history and diverse population contribute to its dynamic cultural scene.
2. Maracaibo
Located in the northwestern region of Venezuela, Maracaibo is the country's second-largest city and is known for its oil industry. The city is famous for its hot climate and the iconic Lake Maracaibo, which is the largest lake in Latin America. Maracaibo is also renowned for its folkloric music and vibrant festivals, such as the Feria de la Chinita, celebrating the city's patron saint.
3. Valencia
Valencia is an important industrial city situated in the Carabobo state. It is known for its manufacturing sectors and is often referred to as the "Carabobo Industrial Center." Valencia also boasts beautiful parks and gardens, such as the Parque Fernando Peñalver, and a rich history reflected in its architecture, making it a blend of urban and natural beauty.
4. Barquisimeto
As the capital of Lara state, Barquisimeto is known for its cultural contributions, particularly in music and art. The city hosts numerous events and festivals, including the famous Festival de la Salsa. It is also home to the iconic Barquisimeto Cathedral, recognized for its modern architectural style, making the city a center of creativity in Venezuela.
5. Maracay
Maracay is situated near the coast and serves as the capital of Aragua state. Known for its pleasant climate and green spaces, Maracay is often called the "Garden City." The city is surrounded by the Henry Pittier National Park, offering numerous recreational opportunities for residents and visitors alike.
6. Mérida
Nestled in the Andes mountains, Mérida is known for its stunning natural beauty and as a center for adventure tourism. It is famous for its cable car, one of the highest and longest in the world, providing breathtaking views of the surrounding mountains. Mérida also has a vibrant university culture, contributing to its youthful and lively atmosphere.
7. Puerto Ordaz
Puerto Ordaz, located on the banks of the Orinoco River, is part of the city of Ciudad Guayana. It is an industrial hub, especially for the iron and aluminum industries. The city is characterized by its modern infrastructure and proximity to natural wonders like the La Llovizna National Park, which features beautiful waterfalls and lush landscapes.
8. Ciudad Guayana
Founded in 1961, Ciudad Guayana is a planned city formed from the merger of Puerto Ordaz and San Félix. It serves as an industrial center and is strategically located near significant natural resources. The city is notable for its modernist architecture and extensive green spaces, including parks along the Orinoco River.
9. Cumana
Cumana, the capital of Sucre state, is one of the oldest cities in Venezuela, founded in 1515. Known for its rich history and colonial architecture, Cumana boasts beautiful beachesnearby, making it a popular tourist destination. The city is often called "La Tierra de la Virgen de la Candelaria" and hosts vibrant cultural festivities.
10. San Cristóbal
San Cristóbal is the capital of Táchira state, situated in the Andean region. The city is known for its pleasant climate and proximity to the Colombian border, making it a significant commercial hub. San Cristóbal is rich in folklore and traditional crafts, contributing to its unique cultural identity.
Regions On The Map Of Venezuela
1. Andes
The Andes region in Venezuela is characterized by its stunning mountainous landscapes, including peaks that rise over 5,000 meters. This region is rich in biodiversity and features several indigenous communities. The Andes are also known for agriculture, with coffee and fruits being major crops. Key cities in this region include Mérida and San Cristóbal.
2. Llanos
The Llanos, or plains, is an extensive flat region located in the central part of Venezuela. This area is known for its vast grasslands and is crucial for cattle ranching and agriculture. The Llanos are also home to a variety of wildlife, making it an important ecological zone. The region experiences distinct wet and dry seasons, influencing local farming practices.
3. Amazon
Venezuela's Amazon region is part of the larger Amazon rainforest, one of the most biodiverse areas on the planet. This region is home to numerous indigenous groups and is characterized by dense vegetation, rivers, and unique wildlife. The Amazon is critical for global ecological balance, playing a key role in carbon storage and biodiversity.
4. Caribbean Coast
The Caribbean coast of Venezuela is known for its beautiful beaches, warm climate, and vibrant tourist activity. This region includes popular destinationslike Margarita Island and Los Roques National Park, attracting visitors for its stunning landscapes and recreational opportunities. The coast is also significant for fishing and agriculture.
5. Guiana Highlands
The Guiana Highlands are located in the southeastern part of Venezuela, featuring unique table-top mountains and stunning waterfalls, including Angel Falls. This region is relatively untouched and known for its rich biodiversity, with many endemic species. The highlands are also home to several indigenous communities that maintain traditional lifestyles.
Population Of Venezuela
As of recent estimates, Venezuela has a population of approximately 28 million people. This diverse population is composed of various ethnic groups, including mestizos, Europeans, Africans, and indigenous peoples. The distribution of the population varies significantly across the country, with most people residing in urban areas, particularly in and around major cities like Caracas and Maracaibo.
The population density in urban areas can lead to bustling metropolitan environments, while rural regions may have a more sparse population. Understanding the population distribution is crucial for grasping the social dynamics and cultural influences that shape life in Venezuela.
Language Of Venezuela
The official language of Venezuela is Spanish, and it is spoken by the overwhelming majority of the population. Spanish in Venezuela has its own distinct features, influenced by the country’s history and interactions with indigenous groups, as well as its proximity to Caribbean culture.
- Venezuelan Spanish: The Spanish spoken in Venezuela has some unique regional dialects and expressions. In general, Venezuelan Spanish is known for its warm and informal tone, with common expressions like “chévere” (cool) and “pana” (friend).
- Indigenous Languages: Although Spanish is the dominant language, Venezuela is home to several indigenous groups, and as a result, indigenous languages such as Wayuu, Yekwana, and Pemonare spoken in some regions of the country. These languages are recognized by the Venezuelan constitution, which grants protection to indigenous cultures and their languages.
- Foreign Languages: Due to its historical ties and international relations, other languages, such as English, Italian, and Portuguese, are also spoken by some communities, especially in urban centers and among expatriates.
Despite the dominance of Spanish, the country’s linguistic diversity is an important part of its cultural heritage.
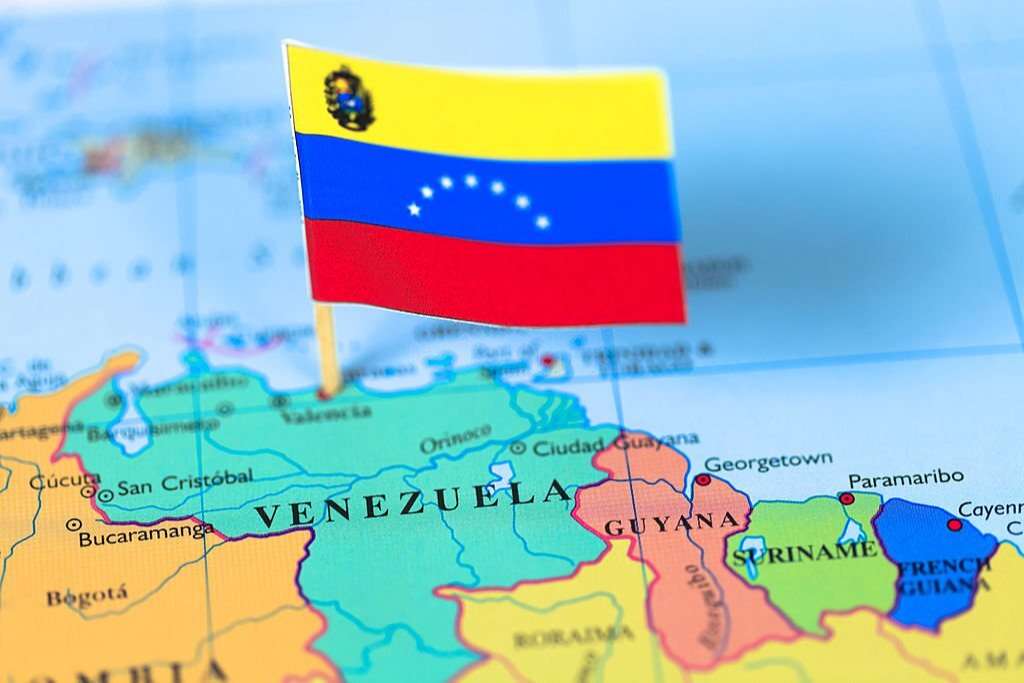
Flag Of Venezuela
The flag of Venezuelais a powerful symbol of the country’s history and national identity. The flag consists of three horizontal bands of yellow, blue, and red, with eight stars arranged in a semi-circle in the blue band.
- Yellow: Represents the country’s wealth, particularly its gold and natural resources.
- Blue: Symbolizes Venezuela’s struggle for independence and its loyalty to freedom and justice.
- Red: Represents the blood shed by Venezuelans in their fight for independence from Spain.
- Stars: The eight stars represent the eight provinces that constituted Venezuela at the time of its independence from Spain.
Government Of Venezuela
Venezuela is a federal republicwith a presidential systemof government. It is based on the 1999 constitution, which outlines the political and legal structure of the country. The government operates under a framework of separation of powers, with executive, legislative, and judicial branches, but in practice, there have been concerns about the concentration of power in the hands of the president, especially during the tenure of former President Hugo Chávez and his successor Nicolás Maduro.
- Executive Branch: The President of Venezuela serves as both the head of state and head of government. The President is elected by popular vote for a six-year term and can be re-elected. The President appoints vice presidents and other government officials.
- Legislative Branch: The National Assembly(Asamblea Nacional) is a unicameral legislature made up of elected representatives. It plays a crucial role in law-making, but tensions between the legislative and executive branches have led to political conflicts, especially in recent years.
- Judicial Branch: The Venezuelan judicial system is headed by the Supreme Court of Justice(Tribunal Supremo de Justicia), which is responsible for interpreting laws and overseeing the constitutionality of government actions.
Venezuela's government has been a subject of international controversy due to accusations of authoritarianism and human rights abuses. The political crisis in the country has resulted in widespread protests, economic collapse, and mass emigration.
Currency Of Venezuela
The official currency of Venezuela is the Venezuelan Bolívar(symbol: Bs. or VEF), which has gone through significant devaluations and changes over the years due to the country’s economic crisis.
- Bolívar Soberano (VES): In 2018, Venezuela introduced a new currency, the Bolívar Soberano, as part of an effort to combat hyperinflation. This was a redenomination of the previous Bolívar Fuerte, which had lost much of its value due to skyrocketing inflation rates.
- Hyperinflation and Dollarization: Venezuela has been experiencing hyperinflationfor several years, leading to the widespread adoption of the US dollar in many parts of the economy. Although the bolívar is still legal tender, many transactions, especially for larger purchases, are conducted in US dollars or other foreign currencies.
- Cryptocurrency: Venezuela has also turned to cryptocurrencyas an alternative due to the lack of confidence in the bolívar. The country has even launched its own cryptocurrency, the Petro, though its success and effectiveness have been questioned.
Despite efforts to stabilize the currency, the economy of Venezuela continues to struggle, and the bolívar remains highly volatile.
Dialing Code Of Venezuela
Venezuela’s international dialing code is +58. When calling Venezuela from abroad, you would need to dial this country code followed by the specific area code and phone number.
- Mobile and Landline Phones: Venezuela uses different area codes for various regions, with Caracas, the capital, having the area code 0212. Mobile numbers typically begin with the prefix 04, followed by the rest of the number.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure: The telecommunications system in Venezuela has faced challenges in recent years due to the economic crisis, but mobile phone use and internet access remain widespread, despite intermittent service disruptions.
Total Area Of Venezuela
Venezuela covers a total area of approximately 916,445 square kilometers (353,841 square miles), making it the 33rd largest country in the world. This substantial area encompasses a variety of geographical features, from the rugged Andes mountains to the flat plains of Los Llanos and the dense jungles of the Amazon basin.
The total area is divided into several distinct regions, each contributing to the country's rich natural and cultural heritage. The sheer size of Venezuela allows for a diverse range of climates and ecosystems, influencing everything from agriculture to tourism.
High Roads And Desert
1. La Trinchera
La Trinchera is a significant highway that connects the Andean region with the central plains. This high road is known for its breathtaking views of the mountainous landscapes and lush valleys. Travelers along this route can experience the diverse flora and fauna of Venezuela.
2. Táchira-San Cristóbal Road
The Táchira-San Cristóbal road is a crucial route for trade and travelbetween Venezuela and Colombia. This road traverses landscapes and is often busy with commercial traffic. The area is known for its agriculture, particularly coffee and flowers, contributing to its economic importance.
3. Los Médanos De Coro
While not a high road, the Médanos de Coro is a significant desert-like area in Venezuela, known for its stunning sand dunes and unique ecosystem. This region is a UNESCO World Heritage site and offers opportunities for adventure tourism, including sandboarding and wildlife observation.
National Parks
1. Canaima National Park
Canaima National Park is one of the largest national parks in the world, famous for its stunning landscapes, including waterfalls and table-top mountains. Home to Angel Falls, the park attracts adventure seekers and nature lovers, offering opportunities for hiking, camping, and exploring its diverse ecosystems.
2. Henri Pittier National Park
Located near Maracay, Henri Pittier National Park is known for its rich biodiversity, featuring a mix of tropical forests and coastal ecosystems. It is home to numerous bird species and offers various hiking trails. The park plays a vital role in conservation efforts and is a favorite among ecotourists.
3. Morrocoy National Park
Morrocoy National Park features beautiful beaches, coral reefs, and mangrove ecosystems. Located on the coast, this park is popular for water sports, birdwatching, and relaxation. Its diverse habitats support a wide range of wildlife, making it an essential area for conservation.
4. Roraima National Park
Roraima National Park is famous for its dramatic landscapes, including the iconic Roraima Mountain. This park offers trekking opportunities and is a hotspot for biodiversity. The unique tepuis (table-top mountains) and diverse flora and fauna make it a must-visit for nature enthusiasts.
5. Sierra Nevada National Park
Sierra Nevada National Park is known for its high-altitude landscapes, rich biodiversity, and endemic species. This park offers hiking trails and is home to Venezuela's highest peaks. The diverse ecosystems range from cloud forests to paramo (high-altitude grasslands), providing stunning scenery and unique wildlife experiences.
Venezuela Tourist Attractions Map
The map of Venezuelahighlights tourist attractions showcasing the country's beauty and cultural heritage. For those interested, virtual traveloffers an immersive glimpse into destinations like Angel Falls, the Andes, and Caracas:
- Angel Falls: The world's highest uninterrupted waterfall, located in Canaima National Park, is a must-see for any visitor.
- Los Roques National Park: This stunning archipelago is known for its crystal-clear waters and white sandy beaches, perfect for water sports and relaxation.
- Roraima: A unique tabletop mountain that attracts hikers and adventure seekers from around the globe.
These attractions not only offer breathtaking views but also provide insight into Venezuela's diverse ecosystems and rich cultural traditions.
Venezuela Economy
Venezuela's economy is primarily based on its vast natural resources, particularly oil. The country holds some of the largest proven oil reserves in the world, which significantly influences its economy. Oil production accounts for a substantial portion of Venezuela's GDP and exports.
Fun facts about Venezuelainclude its rich cultural diversity, stunning natural attractions, and diverse ecosystems, from the Andes mountains to the Caribbean coastline. These elements make Venezuela a unique and fascinating place to explore.
In addition to oil, Venezuela's economy relies on agriculture, mining, and manufacturing. The diversity in economic activities is reflected on the map, as different regions specialize in various industries, shaping the livelihoods of their inhabitants.
Collapse And Current Challenges
Venezuela has faced significant socio-economic challenges in recent years, leading to a severe crisis that has impacted its citizens and economy. Issues such as hyperinflation, political instability, and shortages of essential goods have created a complex situation. This collapse has altered the geographical and social landscape of the country, leading to mass migration and changes in demographic patterns.
The challenges faced by Venezuela today are evident on the map, as many areas experience different levels of access to resources, services, and opportunities. Understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping the current state of Venezuela and the resilience of its people.
Interesting Facts About Venezuela
- Venezuela is home to the world's highest waterfall, Angel Falls, which drops 3,212 feet.
- The country boasts some of the largest oil reserves globally, significantly influencing its economy.
- Venezuela is one of the few countries where the Andes mountains meet the Caribbean Sea.
- The country's official language is Spanish, but many indigenous languages are also spoken.
- Venezuela has the largest natural gas reserves in South America.
- The country is known for its diverse wildlife, including the rare Orinoco crocodile.
- Venezuela’s national dish is arepas, a cornmeal cake filled with various ingredients. Romantic vacationspots in Venezuela, like Los Roques and Canaima National Park, offer beautiful, serene settings for couples.
- The country has a rich cultural heritage, blending indigenous, African, and Spanish influences.
- Lake Maracaibo, located in Venezuela, is the largest lake in Latin America.
- The country experiences one of the highest rates of biodiversity in the world, especially in its national parks.
FAQs
What Are The Major Geographical Features Of Venezuela?
Venezuela features diverse landscapes, including the Andes mountains, the Amazon rainforest, extensive plains (Llanos), and a beautiful Caribbean coastline.
How Is Venezuela Divided Politically?
Venezuela is divided into 23 states and a capital district, with each region having its own local government and administrative structure.
What Are The Most Visited Cities In Venezuela?
The most visited cities include Caracas, Maracaibo, Valencia, and Mérida, each offering unique attractions and cultural experiences.
How Does Venezuela’s Geography Influence Its Culture?
Venezuela’s varied geography contributes to its rich cultural diversity, as different regions host distinct traditions, languages, and lifestyles influenced by their environments.
What Natural Wonders Can Be Found In Venezuela?
Venezuela is home to numerous natural wonders, including Angel Falls, Los Roques National Park, Roraima, and the vast Amazon rainforest.
Conclusion
Venezuela's map offers a glimpse into its diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage. From the bustling capital of Caracas to the breathtaking beauty of Angel Falls, each area provides a unique perspective on the lives of its people and the natural resources that define the nation.
By examining the cities, regions, and national parks, readers can appreciate what Venezuela has to offer. The intricate details of its map tell a compelling story, a narrative that embodies the spirit and resilience of its people.
Jump to
Geographical Overview Of Venezuela
Capital Of Venezuela
Map Of Venezuela Cities
Regions On The Map Of Venezuela
Population Of Venezuela
Language Of Venezuela
Flag Of Venezuela
Government Of Venezuela
Currency Of Venezuela
Dialing Code Of Venezuela
Total Area Of Venezuela
High Roads And Desert
National Parks
Venezuela Tourist Attractions Map
Venezuela Economy
Collapse And Current Challenges
Interesting Facts About Venezuela
FAQs
Conclusion

Finn Wilde
Author
For Finn Wilde, the wilderness is more than just a destination - it’s a way of life. Over the past decade, he has led multiple expeditions in some of the world’s most remote regions, from the icy fjords of Greenland to the rugged trails of Patagonia.
Finn emphasizes sustainability in all of his adventures, helping participants connect with nature while promoting responsible exploration. His expeditions inspire individuals to explore the great outdoors while fostering a deep respect for the environment.

Michael Rachal
Reviewer
Michael Rachal believes that luxury lies in the details. With over 20 years of experience in the luxury travel industry, he has crafted hundreds of bespoke itineraries for clients seeking personalized, unforgettable experiences.
Whether guiding clients through private cultural tours or curating culinary journeys with world-renowned chefs, Michael ensures that each trip is tailored to perfection.
His ability to anticipate needs and exceed expectations has earned him a reputation as a leading expert in luxury travel.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles