Australia And South Pacific Map - Find Out More About These Paradise Islands
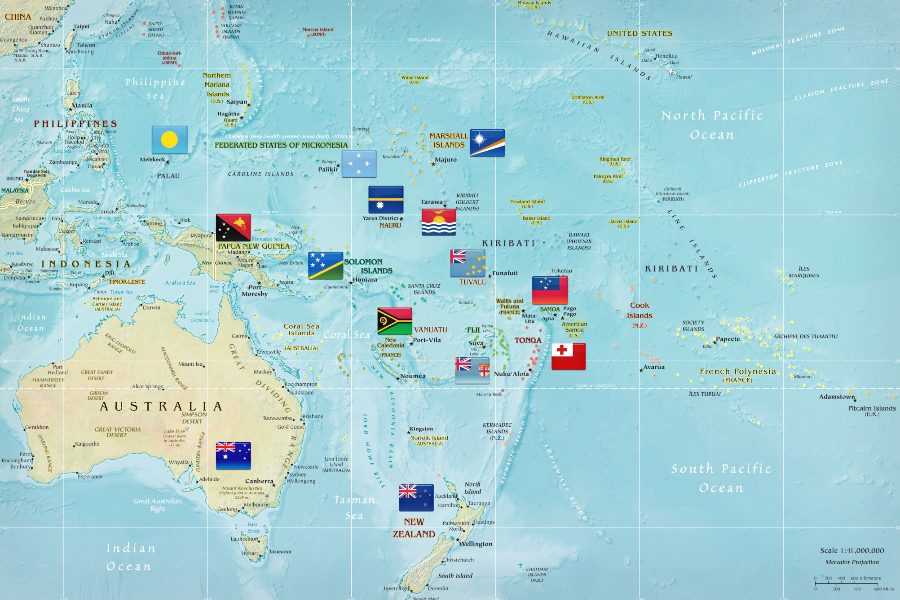
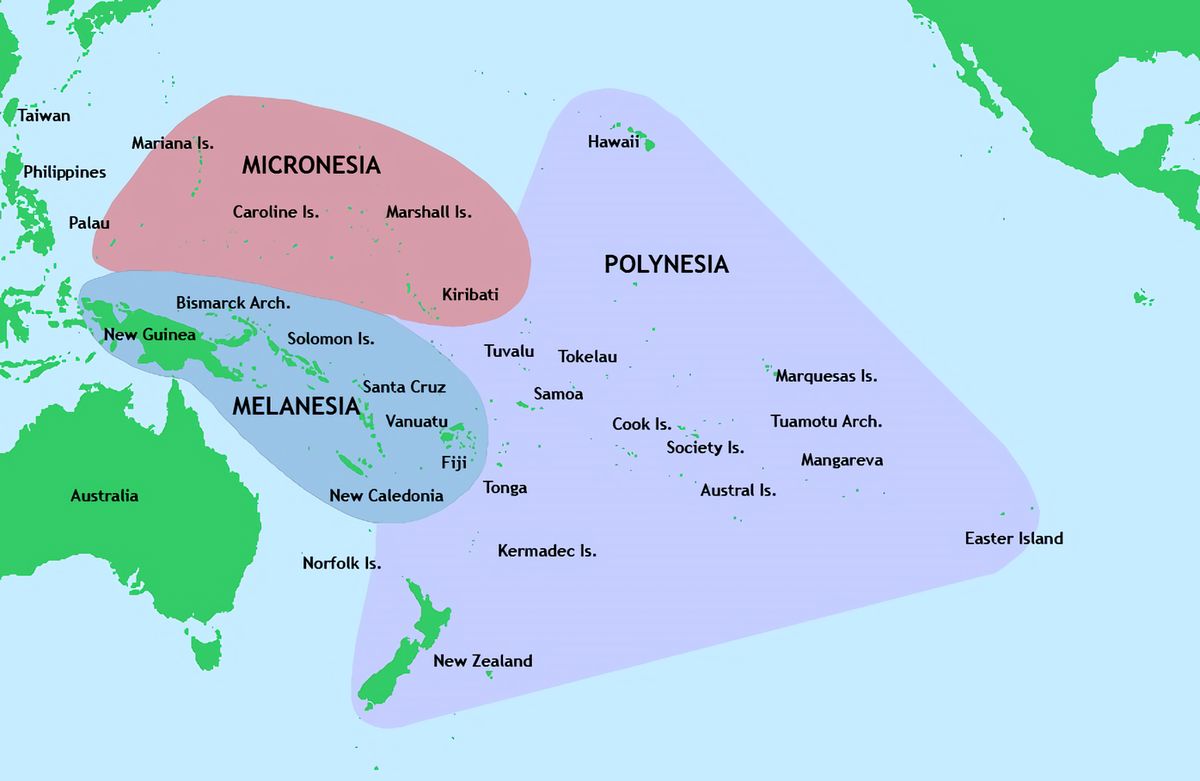
Australia and South Pacific map may be a little confusing for some people. Not only these group of islands are scattered all over the Pacific, but these islands are undeniably different in many ways. Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia are the three major groups of islands based on physical geography, local inhabitants, and location.
Author:Velma BattleReviewer:Michael RachalJul 11, 2022214 Shares213.7K Views
Australia and South Pacific mapmay be a little confusing for some people. Not only these group of islands are scattered all over the Pacific, but these islands are undeniably different in many ways.
Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia are the three major groups of islands based on physical geography, local inhabitants, and location.
Although indigenous cultural legacy is still prevalent in the South Pacific, Western civilization has made significant inroads into people's lives. The globalization trend has a significant impact on the economic conditions that drive Pacific cultural dynamics.
Australia Facts
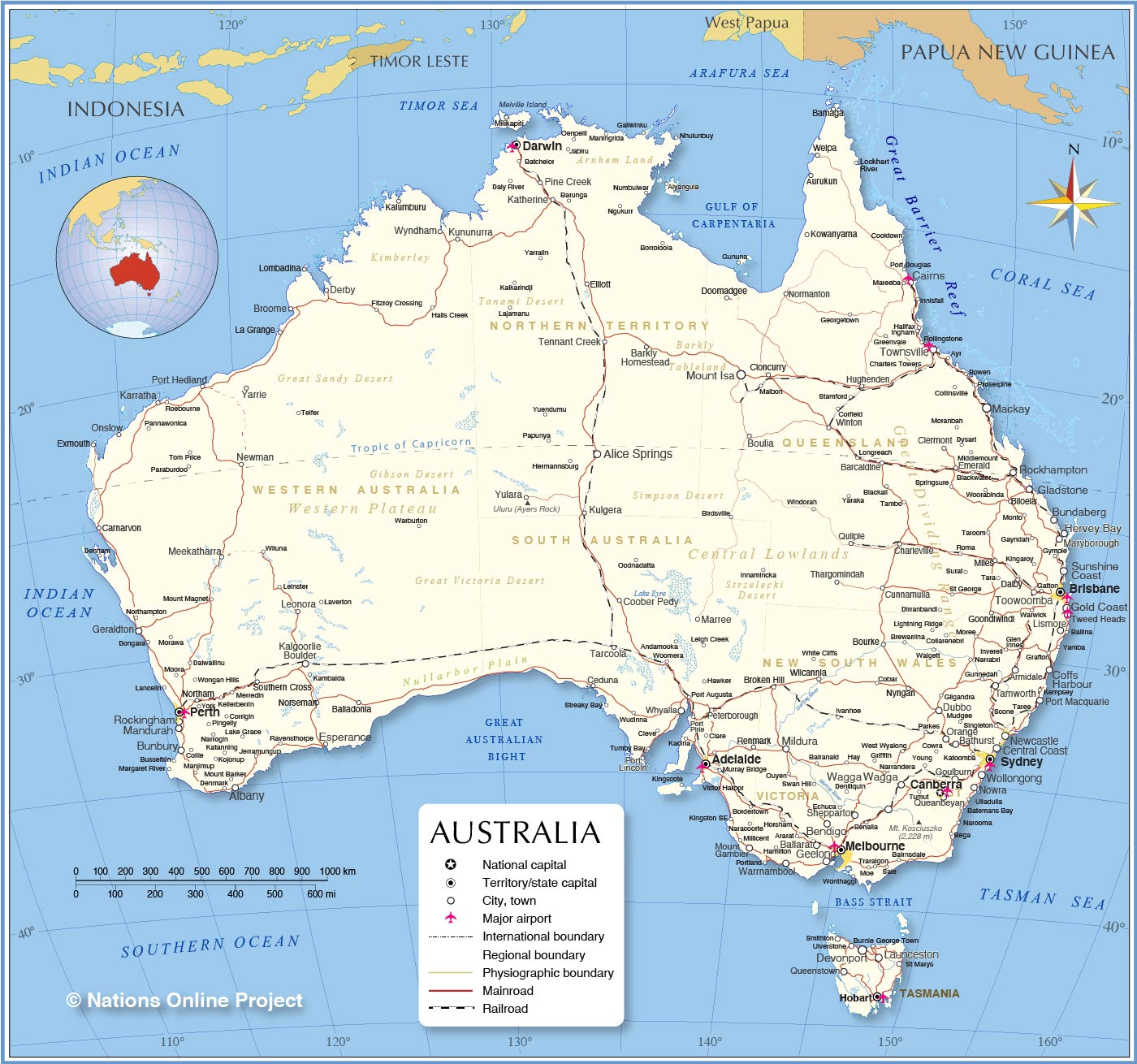
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, consists of the Australian mainland, Tasmania, and several islands. Australia is the largest country in Oceania and the sixth-largest in the globe.
Australia is the oldest, flattest, driest, least fertile inhabited continent. This megadiverse country has deserts in the center, tropical rainforests in the north-east, and mountain ranges in the south-east.
65,000 years ago, indigenous Australians populated the continent. Early 17th-century Dutch explorers began European naval exploration of Australia. In 1770, Great Britain seized Australia's eastern half and established it by penal transportation to New South Wales on 26 January 1788, Australia's national day.
By the 1850s gold rush, European settlers had explored most of the continent and founded five self-governing crown colonies. On 1 January 1901, six colonies united to establish Australia. Australia has a stable liberal democracy and prosperous market economy.
Australia is a constitutional monarchy with six states and 10 territories. Australia's 26 million people live mostly in cities along the east coast. Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide are the five major cities.
Australia's demography has been changed by centuries of immigration; 30% of the country's population are immigrants, the greatest proportion among major Western nations.
South Pacific Facts
The umbrella term Pacific Islands has numerous connotations. It is sometimes used to refer simply to the islands defined as being in Oceania.
At times, it refers to Pacific Ocean islands that were previously colonized by the British, French, Spaniards, Portuguese, Dutch, or Japanese, or by the United States. Pitcairn Islands, Taiwan, and Borneo are a few examples.
Oceanic islands in Melanesia, Micronesia, Polynesia, and the eastern Pacific are included in a generally used biogeographic definition. These are commonly referred to as the "Tropical Pacific Islands." Ecologists Dieter Mueller-Dombois and Frederic Raymond Fosberg classified the Tropical Pacific Islands into the following categories in the 1990s.
Australia And South Pacific Map
Oceania is a region in the Pacific Ocean is a geographical region composed of Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia.
Oceania is predicted to have a land area of 8,525,989 square kilometers (3,291,903 square miles)[discuss] with a population of over 41 million people.
When compared to the continents, Oceania has the smallest land area and, after Antarctica, the second smallest population. Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Auckland, and Adelaide are its six largest populous centers.
Oceania's economies range from the highly developed and globally competitive financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand.
They rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much less developed economies of Kiribati, Papua New Guinea, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, and Western New Guinea,, as well as medium-sized Pacific island economies like Fiji, Palau, and Tonga.
Australia is the largest and most populated country in Oceania, with Sydney as its major metropolis. Puncak Jaya in Papua is the highest point in Oceania, standing at 4,884 meters.
More than 60,000 years ago, the earliest settlers of Australia, New Guinea, and the vast islands to the east arrived.
Oceania was first explored by Europeans beginning in the 16th century. Between 1512 and 1526, Portuguese explorers reached the Tanimbar Islands, some of the Caroline Islands, and west Papua New Guinea.
James Cook, who later arrived in the well developed Hawaiian Islands, sailed to Tahiti and followed the east coast of Australia for the first time on his maiden trip in the 18th century.
During WWII, the Pacific front saw significant conflict, mostly between Allied powers the United States, Philippines (a US Commonwealth at the time), and Australia, and Axis power Japan.
The introduction of European settlers in later centuries significantly altered Oceania's social and political landscape. In more recent times, there has been increased discussion over national flags, as well as a desire by certain Oceanians to exhibit their distinct and independent identity.
Aboriginal Australian rock art is the world's oldest continuously practiced creative tradition. The majority of Oceanian countries are multi-party representative parliamentary democracies, with tourism being a significant source of revenue for Pacific Island states.
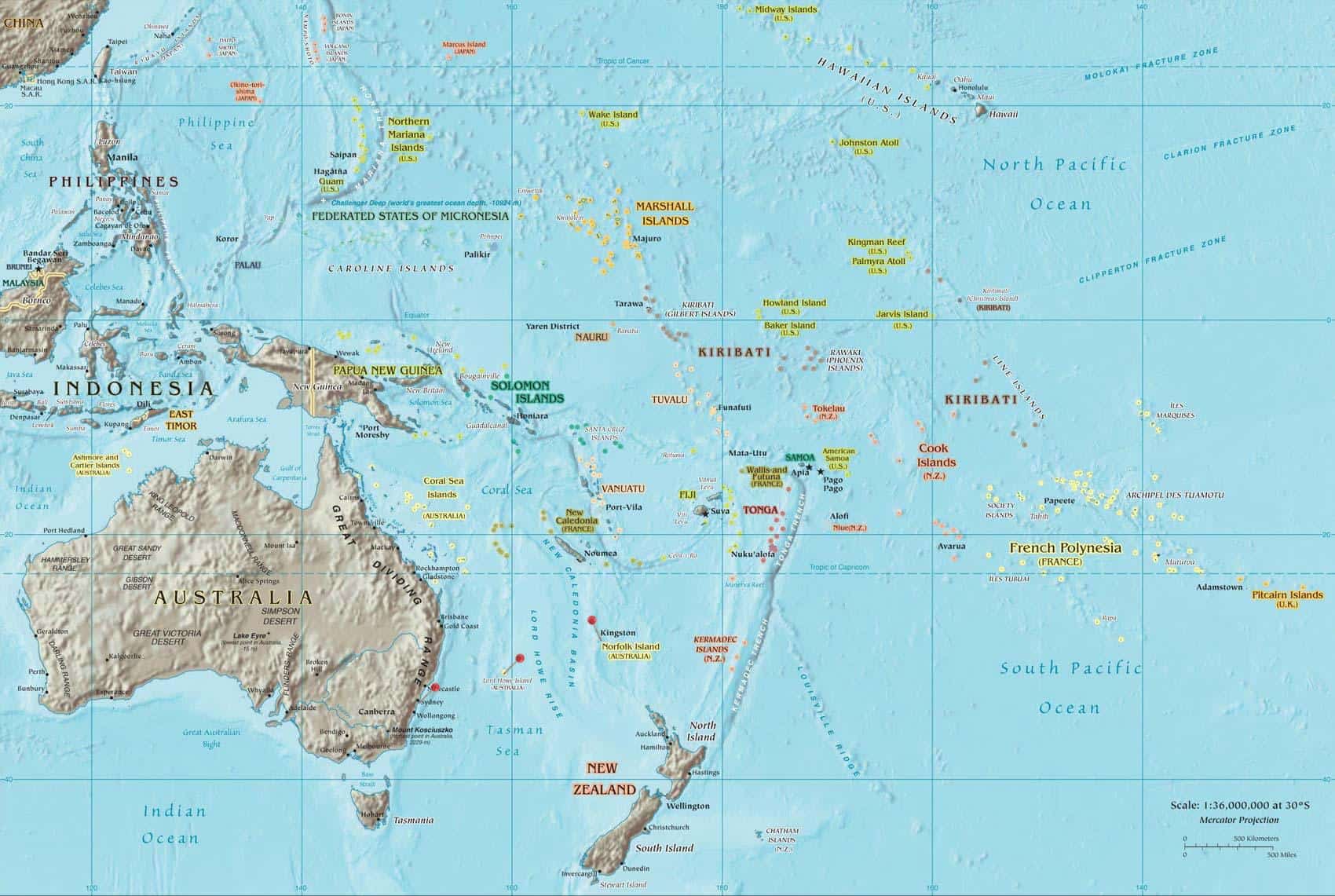
South Pacific Map Countries
Western Melanesia
- The Solomon Islands
- Bougainville and Buka Island
- The Bismarck Archipelago and other islands directly east of New Guinea
Eastern Melanesia
- New Caledonia
- Vanuatu
- The Santa Cruz Islands
Subtropical Islands In The Australia/New Zealand Region
- Norfolk Island
- Lord Howe Island
Micronesia
- The Gilbert Islands (Kiribati)
- The Marshall Islands
- Wake Island
- Nauru and Banaba
- The Caroline Islands
- The Southern Marianas
- The Northern Marianas
- Marcus Island
Central Polynesia
- Tuvalu, Tokelau and the Northern Cook Islands(Pukapuka, Nassau, Rakahanga, Manihiki, Penrhyn, Suwarrow and Palmerston)
- Howland Island, Baker Island, Jarvis Island, Malden Island and Starbuck Island
- The Line Islands
- The Phoenix Islands
- Johnston Atoll
- The Bonin Islands and Volcano Islands
Western Polynesia
- Niue
- Wallis and Futuna
- Samoa
- Tonga
Eastern Polynesia
- The Marquesas Islands
- Easter Island and Salas y Gómez
- The Tuamotu Archipelago and the Pitcairn Islands
- The Society Islands
- The Austral Islands
- The rest of the Cook Islands
Northern Polynesia
The Hawaiian Islands
Oceanic Islands Of The Eastern Pacific
- The Juan Fernández Islands
- The Desventuradas Islands
- The Galápagos Islands
- Clipperton Island
- Cocos Island and Malpelo Island
- The Revillagigedo Islands
People Also Ask
What Area Is The South Pacific?
Southwest Pacific, Central Pacific, and Southeast Pacific surrounded the South Pacific Area. It included Ellice, Phoenix, Marquesas, Tuamotu, Samoa, Fiji, New Hebrides, New Caledonia, and New Zealand.
Is Australia Considered South Pacific?
Oceania is an area comprised of thousands of islands scattered throughout the Central and South Pacific Oceans. It includes Australia, the world's smallest continent by total land area.
Is Australia Connected To The Pacific Ocean?
Asiaand Australia are separated from the Americas by the Pacific. The equator divides it further into northern (North Pacific) and southern (South Pacific) sections. It stretches from Antarctica in the south to the Arctic in the north.
Conclusion
Western fast food, pop music, clothing styles, and social practices frequently dominate television, radio, and film. Invasive Western cultural forces divert attention away from the indigenous culture and legacy of the people who have lived on these secluded islands for millennia.

Velma Battle
Author
Travelling Expert

Michael Rachal
Reviewer
Travelling Expert
Latest Articles
Popular Articles